Filters
What It Is and How It Can Be Managed
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by the appearance of red, thick plaques covered with silvery scales, psoriasis can range from mild forms, which are just a nuisance, to severe forms that affect quality of life. This autoimmune disease is not contagious, but it can be unsightly and uncomfortable for those who suffer from it.
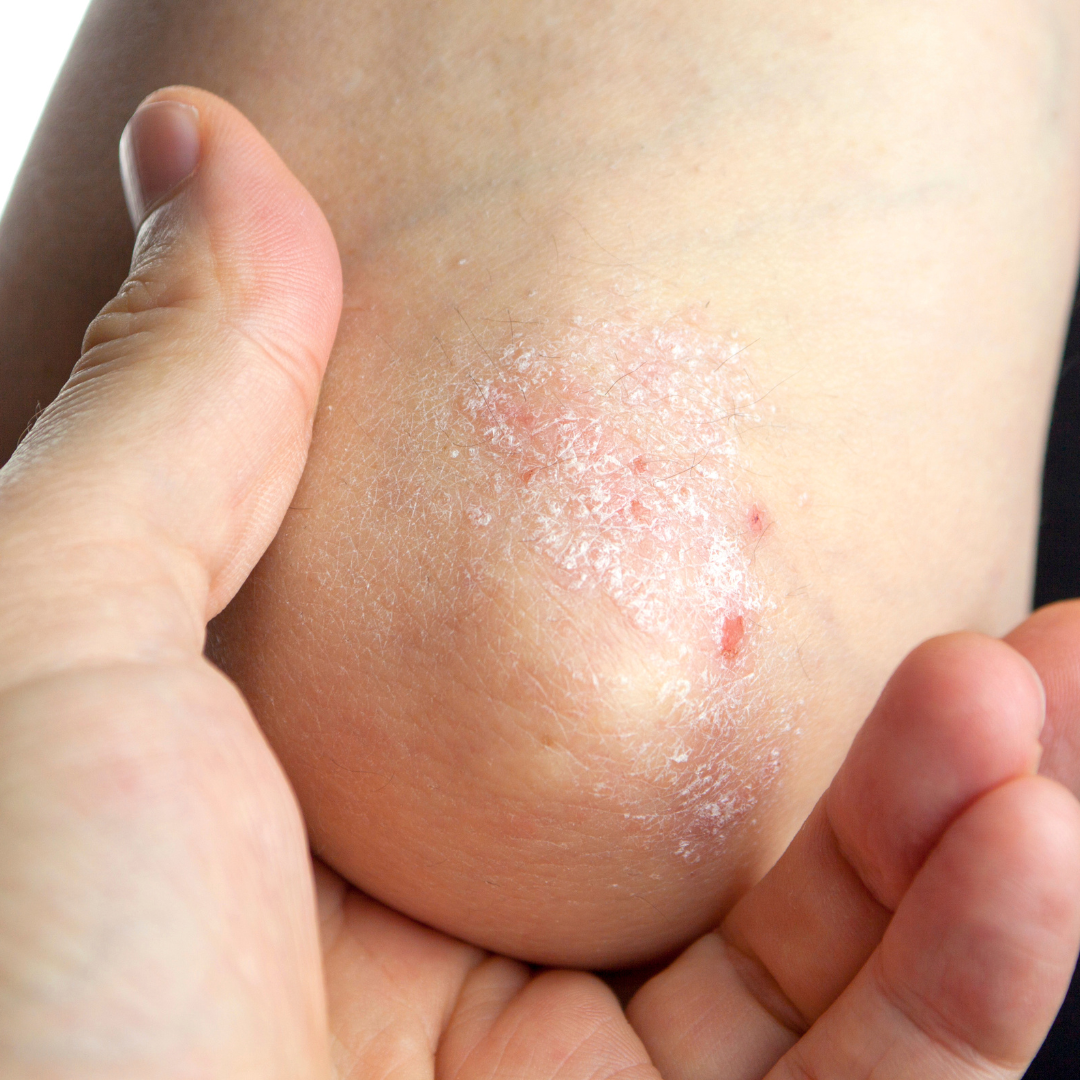
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact causes of psoriasis are not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetics and environmental factors. In people with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to their excessive production. This process accelerates the life cycle of skin cells, causing a rapid buildup of dead cells on the surface of the skin.
Trigger factors may include:
- Stress
- Skin injuries, such as cuts or sunburns
- Infections
- Certain medications
- Alcohol consumption and smoking
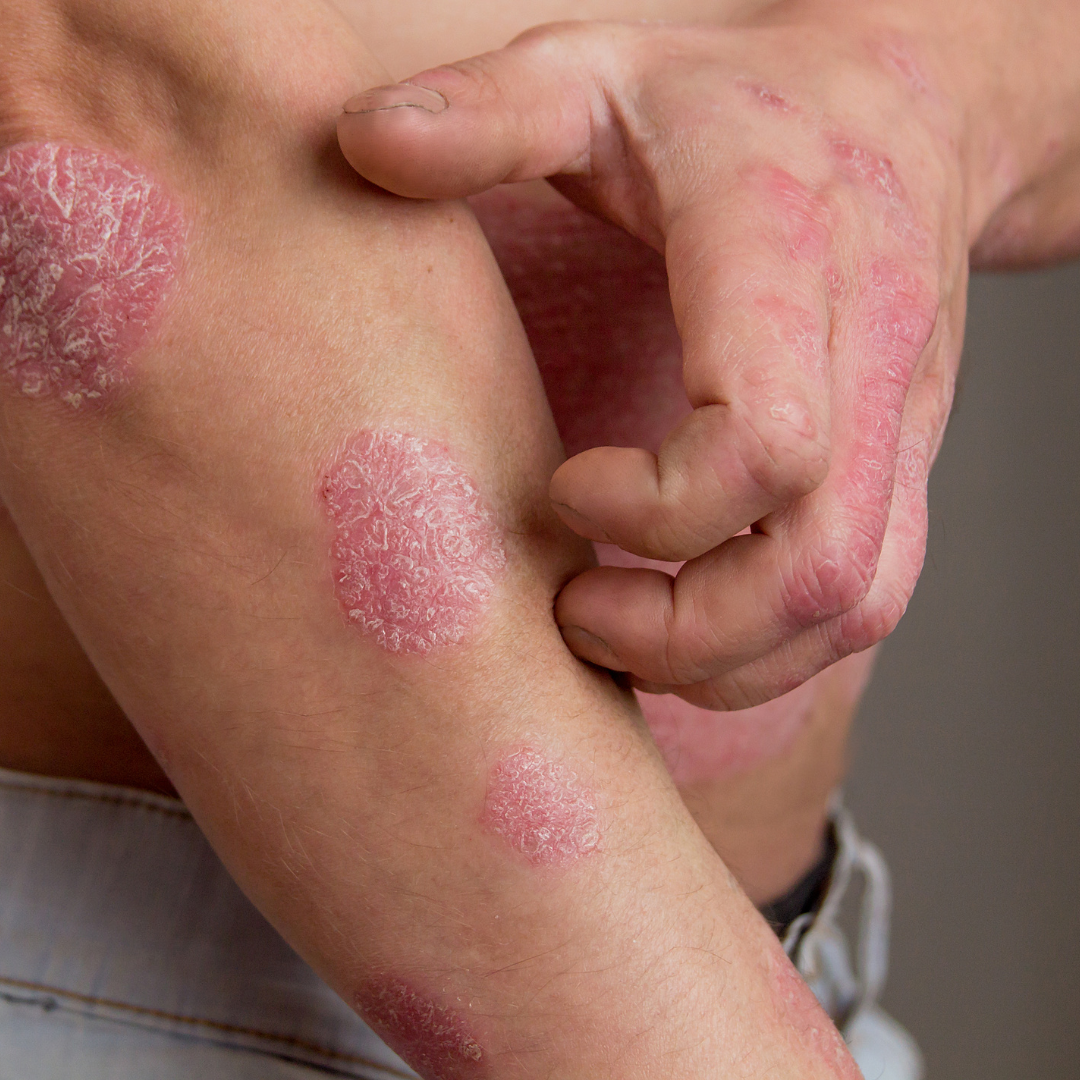
Symptoms of psoriasis
Psoriasis manifests through a variety of symptoms that can vary in severity and appearance, affecting each person differently. This chronic condition can occur on any part of the body and is characterized by episodes of eruptions and periods of remission. Understanding the specific symptoms of psoriasis is crucial to being able to recognize and manage this disease effectively.
Symptoms of psoriasis can vary from person to person, but the most common include:
- Red plates covered with silver scales
- Dry and cracked skin, which may bleed
- Itching, burning, or pain in the affected areas
- Thickened, ridged, or stained nails
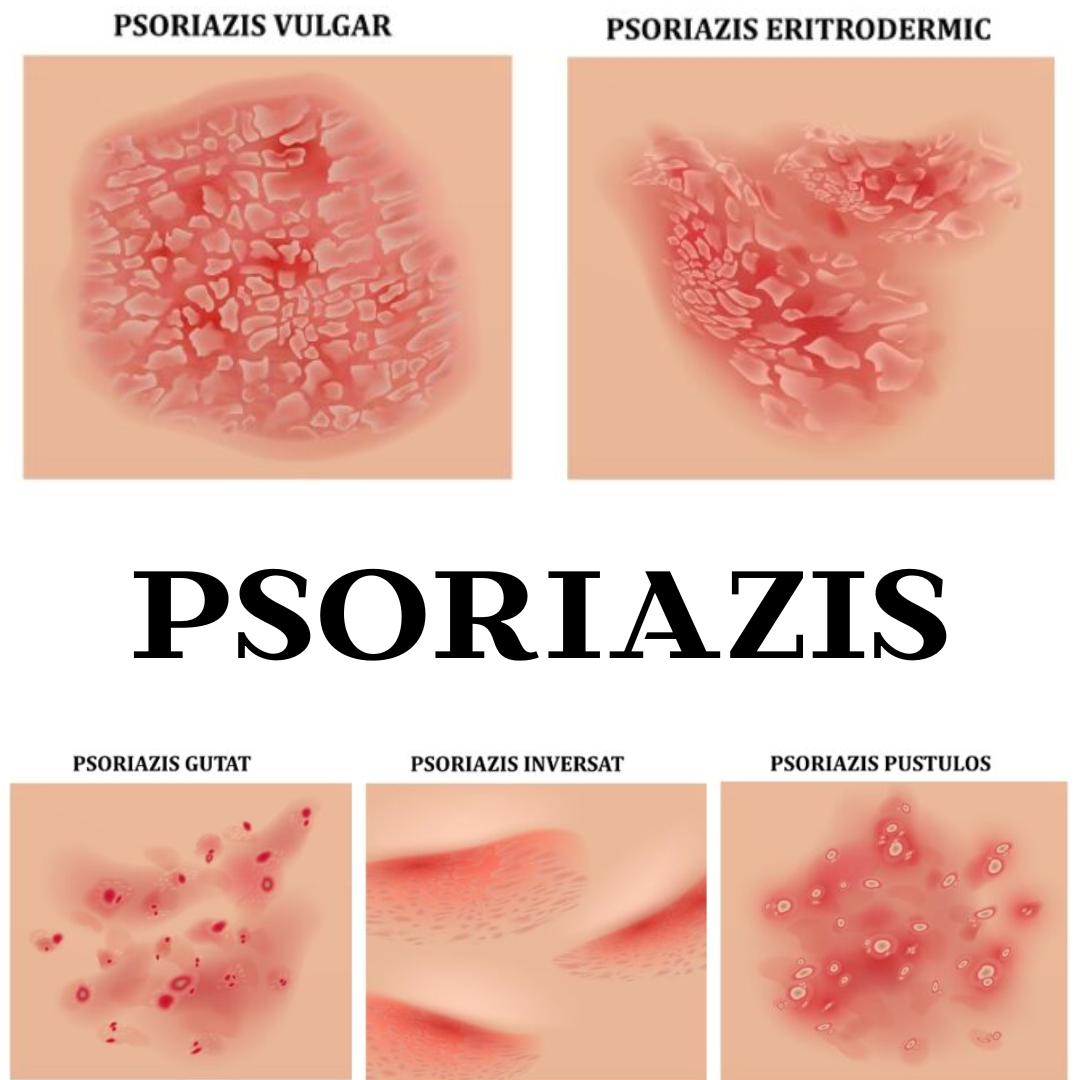
types of psoriasis
Psoriasis presents in several forms, each having its own distinct characteristics:
- Plaque psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris): The most common type, characterized by red plaques covered with scales.
- Guttate psoriasis: Characterized by small, drop-like lesions that appear on the trunk, arms, and legs.
- Inverse psoriasis: Affects skin folds, such as under the arms, in the groin area, and under the breasts.
- Pustular psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: A rare and severe form that can cover the entire body with a red and scaly rash.
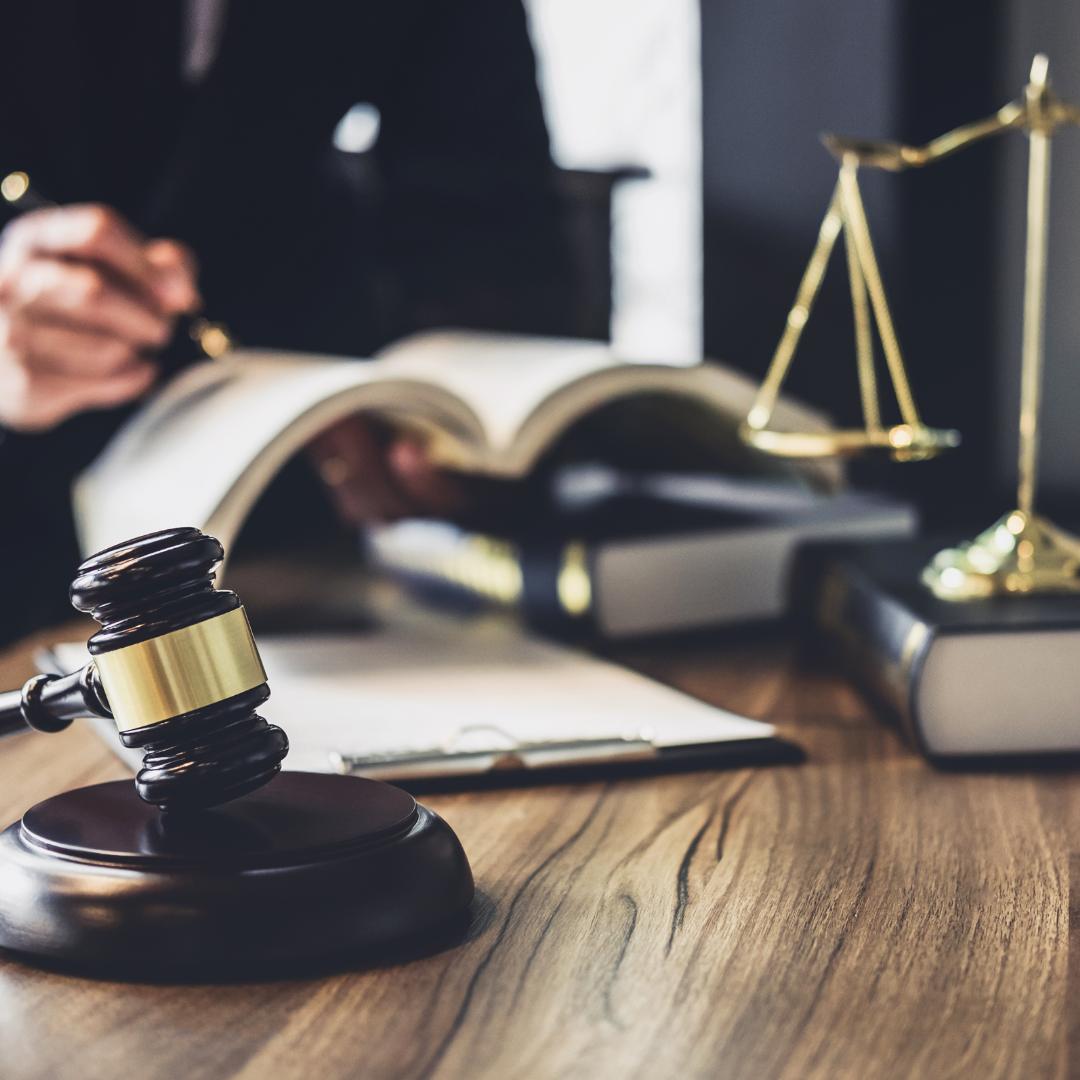

Legislation in Romania
Rights of people with psoriasis
Starting May 1, 2024, insured individuals suffering from psoriasis in Romania will benefit for the first time from compensated medications, provided on an outpatient basis. This is a significant step in supporting patients with psoriasis, ensuring them access to essential treatments without a high financial burden.
(To find out everything about psoriasis medication reimbursement access this link.)
Disability pension for psoriasis
An important precedent was set by the Alba Tribunal, which accepted the request of a man who had initially been rejected by the commission in his attempt to obtain disability classification for psoriasis. The Tribunal accepted the request and classified the man as having a medium degree of disability. This decision highlights that, although uncommon, psoriasis can be considered a sufficiently debilitating condition to justify granting a degree of disability, thus offering new hopes and possibilities to affected individuals facing severe cases.
(Find out more about disability grading for psoriasis by accessing the link.)
do you need help?
frequently asked questions
Unfortunately, there is currently no definitive cure for psoriasis. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition, which means it can persist long-term, with periods of remission and relapse. However, there are numerous treatments available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biological therapies can significantly reduce inflammation, itching, and the appearance of psoriatic plaques. Lifestyle changes, such as stress reduction, a healthy diet, and proper skin care, can also help control the disease.
Although psoriasis cannot be completely cured, with a well-managed treatment plan and under the supervision of a dermatologist, many people manage to keep their symptoms under control and live an active and fulfilling life.
Learn more about psoriasis by clicking the link.
Well, psoriasis is not contagious. It is a chronic autoimmune condition that results from abnormal activity of the immune system. Psoriasis cannot be transmitted from one person to another through physical contact, sharing personal items, or other daily contact methods.
Despite its sometimes severe appearance, which may include red plaques covered with scales, psoriasis is not an infection and cannot be "caught" from someone. Understanding this fact is important to reduce stigma and to support people suffering from this condition.
To convince yourself that psoriasis is not contagious, click the link.
The diagnosis of psoriasis is based on a combination of physical examination, the patient's medical history, and, in some cases, laboratory tests. Here are the main steps involved in diagnosing psoriasis:
1. Physical examination
A dermatologist will carefully examine the skin, scalp, and nails to identify the characteristic signs of psoriasis. These signs may include red, thick plaques covered with silvery scales, dry and cracked skin that may bleed, and changes in the nails, such as pitting (small dents) or separation of the nail from the nail bed.
2. Medical history
The doctor will discuss with the patient the symptoms they are experiencing, their duration, and any known triggering factors, such as stress, infections, certain medications, or skin injuries. The doctor will also ask about the family history, as psoriasis may have a genetic component.
3. Skin biopsy
In some cases, to confirm the diagnosis, the dermatologist may take a small skin sample (biopsy) from an affected area. This sample is then examined under a microscope to determine if the structure of the skin cells is characteristic of psoriasis. The biopsy can help exclude other skin conditions, such as eczema or fungal infections.
4. Laboratory test
Although blood tests are not used to directly diagnose psoriasis, they may be recommended to rule out other conditions or to assess the patient's overall health. In cases of psoriatic arthritis, blood tests can help detect inflammatory markers.
5. Severity Assessment
Once psoriasis is diagnosed, the doctor will assess the severity of the disease. This may include measuring the affected body surface area, evaluating the impact on quality of life, and the degree of inflammation present. Assessing severity helps determine the appropriate treatment.
6. Differential diagnosis
It is important to differentiate psoriasis from other skin conditions that may have similar symptoms. The dermatologist will consider other possible diagnoses, such as seborrheic dermatitis, lichen planus, or atopic dermatitis, and will use physical examination and laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis.
Early and accurate diagnosis of psoriasis is essential for effective disease management. If you suspect you have psoriasis or experience unusual skin symptoms, it is important to consult a dermatologist for a comprehensive evaluation and to receive an appropriate treatment plan.
Yes, psoriasis can also affect children. Although psoriasis is more commonly diagnosed in adults, children and adolescents can also develop this chronic skin condition. Psoriasis in children may present some differences in manifestation and severity compared to adults, but it has many common features.
How does psoriasis manifest in children?
Symptoms of psoriasis in children can vary, but often include:
- Red, thick plaques covered with silvery scales: These most commonly appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
- Small, drop-like skin lesions: This type of psoriasis, known as guttate psoriasis, is more common in children and adolescents and can be triggered by streptococcal infections.
- Itching and discomfort: Children may experience intense itching, which can affect sleep and daily activities.
- Changes in nails: Some children may develop pitting (small pits) on the nails or separation of the nail from the nail bed.
- Dry and cracked skin: Affected areas may become dry and cracked, sometimes bleeding.
Diagnosis of psoriasis in children
The diagnosis of psoriasis in children follows procedures similar to those used for adults. The dermatologist will examine the child's skin, consider the family history and symptoms, and may perform a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of psoriasis in children
Treatment of psoriasis in children may include:
- Topical treatments: Creams and ointments with corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and calcineurin inhibitors are used to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light (UVB) can be effective in reducing symptoms.
- Systemic treatments: In severe cases, systemic medications such as methotrexate and cyclosporine may be used.
- Biologics: For severe forms of psoriasis, biologic drugs that target specific components of the immune system can be an option.
Yes, moderate sun exposure can be beneficial for people with psoriasis. Natural sunlight contains ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can help reduce psoriasis symptoms by slowing down the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation. Many people with psoriasis notice an improvement in their skin condition after sun exposure.
However, it is important to expose yourself to the sun with caution:
- Moderate exposure: Start with short exposure sessions, about 10-15 minutes per day, and monitor how your skin reacts.
- Sun protection: Use sun protection on areas of skin not affected by psoriasis to prevent sunburn, which can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Avoiding burns: Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and make sure you do not get sunburned, as sunburns can trigger or worsen psoriatic lesions.
- Consult a specialist: Talk to your dermatologist about sun exposure and follow their advice, especially if you are using treatments that can sensitize the skin to UV light.
- Phototherapy: In some cases, dermatologists recommend controlled UVB phototherapy, which is a form of treatment with artificial light and is similar to exposure to sunlight, but under controlled medical conditions.
Learn more about sun exposure if you have psoriasis by clicking the link.
Psoriasis does not only affect the skin; it can also have other systemic complications that can significantly influence the quality of life. One of the most serious complications associated with psoriasis is psoriatic arthritis, but there are also other health problems that can arise in connection with this condition.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the joints that occurs in approximately 30% of people with psoriasis. It can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling of the joints, commonly affecting the joints of the fingers, hands, knees, and feet. If not properly treated, psoriatic arthritis can lead to joint damage and loss of functionality.
Symptoms of psoriatic arthritis include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Flare and sensitivity in joints
- Pain in the soles or lower back
- Changes in the nails, such as pitting or separation of the nail from the nail bed
Other complications associated with psoriasis
In addition to psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis can be associated with a number of other complications and medical conditions, including:
1. Cardiovascular diseases:
People with psoriasis have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. The chronic inflammation associated with psoriasis can contribute to the formation of atheromatous plaques in the arteries.
2. Metabolic syndrome:
Psoriasis is often associated with metabolic syndrome, which includes a number of risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, insulin resistance, and high cholesterol levels.
3. Psychological problems:
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on mental and emotional health. Social stigma and the aesthetic impact of the disease can lead to depression, anxiety, and decreased self-esteem.
4. Autoimmune diseases:
There is a connection between psoriasis and other autoimmune diseases, such as Crohn's disease and lupus. These conditions share similar immune mechanisms that may predispose individuals to multiple autoimmune disorders.
5. Eye problems:
Psoriasis can also affect the eyes, causing conditions such as conjunctivitis and uveitis, which can lead to irritation, redness, and eye discomfort.
To learn more, read the article about the possible complications of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that can affect both men and women, but there are certain gender differences in the prevalence, severity, and manifestations of this disease.
Prevalence of psoriasis
Studies have shown that psoriasis affects men and women in relatively equal proportions. However, in some geographic regions, the prevalence may vary slightly, either in favor of men or women. For example, certain studies have indicated a slightly higher prevalence of psoriasis among men compared to women, but the differences are not significant on a global level.
Severity of the disease
There is some evidence that the severity of psoriasis may vary between men and women. Men tend to have more severe forms of psoriasis, which require more aggressive treatments. Additionally, men are more likely to develop psoriasis in areas that are difficult to treat, such as the scalp, chest, and back.
On the other hand, women, although they may have less severe forms of the disease, often report a greater impact on quality of life and psychological well-being. Social stigma and the cosmetic effects of psoriasis can be felt more acutely by women, affecting self-esteem and mental health.
Response to treatment
Hormonal differences can also influence the response to treatment. For example, the hormonal fluctuations that women experience during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause can affect the severity and treatment response of psoriasis. Some women may notice an improvement in symptoms during pregnancy, followed by a postpartum exacerbation.
Psoriatic arthritis
Regarding psoriatic arthritis, which is a common complication of psoriasis, the prevalence and severity can vary between men and women. Men are more prone to severe forms of psoriatic arthritis that affect the spine, while women may more frequently have peripheral psoriatic arthritis, which affects the joints of the hands and feet.
Although psoriasis is a chronic condition for which there is no definitive cure, there are numerous measures you can take to prevent flare-ups and keep symptoms under control. Here are some tips that can help you:
1. Manage stress
Stress is a major trigger of psoriasis. Stress management practices, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and other relaxation techniques, can reduce the frequency and severity of episodes.
2. Maintain a healthy diet
A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can reduce inflammation and contribute to overall health. Avoid processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats, which can worsen inflammation.
3. Hydrate yourself properly
Dry skin can worsen psoriasis symptoms. Regularly use moisturizing creams and emollients to keep the skin well hydrated. Also, consume enough fluids to maintain hydration from within.
4. Avoid specific triggers
Pay attention to specific triggers that worsen your symptoms and try to avoid them. These may include certain foods, alcohol, smoking, infections, and certain medications. Identifying and avoiding these factors can help prevent episodes.
5. Protect your skin
Avoid skin trauma, such as cuts, sunburns, and scratches, as these can trigger psoriasis in the affected areas. Use sunscreen and appropriate clothing to protect your skin from injuries.
6. Follow the treatment recommended by the doctor
Adhering to the treatment plan recommended by your doctor is essential to keep psoriasis under control. This may include regular application of topical creams, taking oral or injectable medications, and attending phototherapy sessions.
7. Maintain an active lifestyle
Regular physical exercise not only improves overall health but can also reduce stress and inflammation. Choose physical activities that you enjoy and that are gentle on the skin, such as swimming, walking, or cycling.
8. Monitor your health status
Pay attention to any changes in your health status and report them to your doctor. Some infections or medical conditions can trigger or worsen psoriasis, so prompt treatment of these is important.
9. Avoid alcohol consumption and smoking
Alcohol and smoking can worsen psoriasis symptoms and trigger episodes. Reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption and quitting smoking can help keep the disease under control.
10. Participate in support groups
Support groups for people with psoriasis can offer useful advice and emotional support. Sharing experiences with others who understand what you're going through can be very helpful in managing the disease.
By adopting these preventive measures and maintaining good collaboration with your doctor, you can reduce the frequency and severity of psoriasis episodes and improve your quality of life.
Itching and discomfort caused by psoriasis can be extremely bothersome and can significantly affect quality of life. However, there are several strategies and treatments that can help alleviate these symptoms:
1. Use moisturizing creams
Keeping the skin well hydrated is essential to reduce itching and irritation. Apply a moisturizing cream or ointment daily, preferably immediately after showering, to seal moisture into the skin. Look for fragrance-free products and those for sensitive skin to avoid additional irritation.
2. Apply topical treatments
There are numerous topical treatments available that can help reduce itching and inflammation. Corticosteroid creams and ointments are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Other options include creams with calcipotriene (a vitamin D derivative), coal tar, and topical retinoids.
3. Use cold compresses
Applying cold compresses or ice packs to the affected areas can help reduce itching and inflammation. Wrap an ice pack in a thin towel and apply it to the skin for a few minutes. Avoid applying ice directly to the skin to prevent irritation.
4. Avoid known triggers
Identify and avoid trigger factors that can worsen itching and discomfort. These may include certain foods, stress, smoking, alcohol, and skincare products that contain fragrances or irritating substances.
5. Use therapeutic baths
Baths with colloidal oatmeal flakes, Dead Sea salt, or baking soda can help soothe inflamed skin and reduce itching. Make sure the water is not too hot, as excessive heat can worsen the symptoms.
6. Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce systemic inflammation and psoriasis symptoms. Consume foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and avoid processed foods and refined sugars.
7. Use oral antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help reduce itching, especially at night. They are available over the counter and can be useful for relieving severe symptoms.
8. Practice stress reduction techniques
Stress can worsen the itching and discomfort caused by psoriasis. Stress-reduction practices such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and regular exercise can help manage the symptoms.
9. Wear comfortable clothes
Choose clothes made from soft, natural materials that allow the skin to breathe and avoid synthetic materials that can irritate the skin. Loose clothing can prevent chafing and further irritation of the affected areas.
10. Consult a dermatologist
If the itching and discomfort are severe or persistent, it is important to consult a dermatologist. They may recommend stronger treatments, including systemic or biological therapies, which can help control symptoms in the long term.
Yes, there are several natural remedies that can help manage the symptoms of psoriasis. These can provide relief and can be used alongside medical treatments prescribed by a doctor. Here are some natural remedies that may be beneficial:
1. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties, which can help soothe inflamed skin and reduce redness and itching. Apply pure aloe vera gel directly to the affected areas several times a day.
2. Essential oils
Essential oils, such as tea tree oil, lavender oil, and chamomile oil, have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. Mix a few drops of essential oil with a carrier oil (such as coconut oil or jojoba oil) and apply the mixture to the affected skin.
3. Apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar can help soothe itching and inflammation. Dilute the apple cider vinegar with water in a 1:1 ratio and apply it to the scalp or other affected areas with a cotton pad. Let it sit for a few minutes, then rinse with warm water.
4. Baths with oat flakes
Colloidal oatmeal baths can help soothe irritated skin and reduce inflammation. Add one cup of colloidal oatmeal to the bathwater and soak for 15-20 minutes. Make sure the water is not too hot, as heat can worsen the symptoms.
5. Anti-inflammatory diet
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce inflammation and alleviate psoriasis symptoms. Consume foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and avoid processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats.
6. Fish oil
Fish oil supplements, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate psoriasis symptoms. Consult your doctor before taking supplements to ensure they are safe and suitable for you.
7. Curcumin
Curcumin, an active compound found in turmeric, has strong anti-inflammatory properties. You can add turmeric to your diet or take curcumin supplements, but it is recommended to consult your doctor before starting any new supplement.
8. Natural moisturizer
Use natural moisturizers, such as coconut oil, shea butter, and jojoba oil, to keep the skin well hydrated and to reduce dryness and itching.
9. Stress reduction
Stress can worsen psoriasis, so it is important to adopt stress management techniques. Meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and other relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and prevent psoriasis flare-ups.
10. Moderate sun exposure
Moderate sun exposure can help alleviate psoriasis symptoms due to UV rays that slow down the growth of skin cells. However, avoid excessive exposure and use sunscreen on unaffected areas to prevent sunburn.
Learn more about natural remedies for psoriasis by clicking the link.
Scalp psoriasis is a common form of psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition that causes rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, red plaques covered with silvery scales. This condition can range from mild forms, involving only a few small spots, to severe forms that cover the entire scalp and can extend to the forehead, the back of the neck, and around the ears.
Manifestations of scalp psoriasis:
- Red plates covered with silver scales:
These plaques can vary in size and may be painful or sensitive to touch. The plaques can be isolated or may cover large areas of the scalp.
- Intense itching:
Itching can be severe and persistent, causing scratching of the scalp, which can lead to lesions and secondary infections.
- Dryness and scaling:
The affected scalp lacks hydration and elasticity, which can lead to excessive dryness and the formation of large, thick flakes that come off.
- Bleeding and cracks:
In severe cases, the scalp skin can become so dry and inflamed that it may crack and bleed.
-Pain and sensitivity:
Psoriatic plaques can be painful and may cause tenderness to touch.
- Temporary hair loss:
Scalp psoriasis can lead to temporary hair loss due to inflammation, excessive scratching, and skin lesions. Hair may begin to grow back once the inflammation is treated and symptoms are managed.
Extent of symptoms:
Scalp psoriasis can also affect other adjacent areas, such as the upper part of the forehead, the hairline, the neck, and around the ears.
Find out everything about scalp psoriasis by clicking the link.
If you have scalp psoriasis and intend to dye your hair, it is important to take some precautions to avoid worsening the symptoms and to protect the health of your scalp. Here is what you should know:
1. Consult the dermatologist
Before dyeing your hair, talk to your dermatologist. The doctor can offer personalized advice and recommend products that are less irritating for your sensitive scalp.
2. Choose gentle hair dyes
Opt for ammonia-free and paraben-free hair dyes, which are gentler and less irritating to the skin. Products based on natural ingredients can be a safer alternative. Read the labels carefully and avoid dyes that contain harsh chemicals.
3. Do an allergy test
Before applying the paint to the entire scalp, do an allergy test on a small patch of skin to ensure you will not have an adverse reaction. This is important even for products that claim to be hypoallergenic.
4. Apply a protective barrier
Apply a thin layer of coconut oil, petroleum jelly, or another protective cream on the scalp and along the hairline before applying the dye. This can help protect the skin from irritation.
5. Avoid painting on irritated scalp
Do not dye your hair if you have an active psoriasis outbreak or if the scalp is irritated, inflamed, or cracked. Wait until the skin calms down and the psoriasis plaques have improved.
6. Use products to soothe the scalp
After coloring your hair, use shampoos and conditioners specially formulated for sensitive or psoriasis-affected scalp. Products with aloe vera, tea tree oil, or other soothing ingredients can help reduce irritation.
7. Avoid frequent washing
Frequent hair washing can dry out the scalp and worsen psoriasis. Try to limit washing and use moisturizing shampoos to keep the scalp healthy.
8. Monitor scalp reactions
After dyeing your hair, pay attention to any signs of irritation, itching, or worsening of psoriasis. If you notice these symptoms, consult a dermatologist immediately for appropriate recommendations and treatments.
9. Consider alternatives to dyeing your hair
If hair dye continues to irritate your scalp, consider alternatives such as temporary color sprays, wigs, or hair extensions. These can provide a change of look without the risk of irritation.
10. Post-painting care
After coloring your hair, give your scalp special attention. Use moisturizing treatments and products that help soothe and repair the skin. Avoid using hot air hair dryers and other styling tools that can dry out the scalp.
Yes, scalp psoriasis can lead to temporary hair loss. Although psoriasis does not directly affect the hair follicles, the symptoms and side effects of this condition can contribute to hair loss. Here are some ways scalp psoriasis can cause hair loss:
1. Inflammation and irritation of the scalp
Inflammation and irritation caused by psoriasis plaques can weaken hair follicles and lead to hair loss. In areas affected by thick plaques and scales, the skin can become very inflamed and sensitive, which affects the health of the hair follicles.
2. Excessive scratching
The intense itching associated with scalp psoriasis can lead to excessive scratching, which can injure the scalp and cause hair loss. Constant scratching can cause microtraumas and weaken the hair follicles.
3. Treatments for psoriasis
Certain treatments for psoriasis, such as topical corticosteroids, can contribute, in rare cases, to hair loss when used long-term. Additionally, aggressive treatments or incorrect use of products can irritate the scalp and affect hair health.
4. Removal of scales
In the process of removing thick scales from the scalp, hair can be accidentally pulled out. Thick plaques of psoriasis can adhere to the hair strands, and when these are removed, the hair can be pulled out along with them.
5. Secondary infections
Scalp lesions caused by psoriasis can increase the risk of secondary infections, which can affect hair follicles and lead to hair loss. Bacterial or fungal infections can worsen the condition of the scalp and contribute to hair loss.
Hair loss is usually temporary!
It is important to mention that, in most cases, hair loss caused by scalp psoriasis is temporary. Once the inflammation and irritation are effectively treated and managed, the hair will begin to grow back.
How to prevent and manage hair loss associated with scalp psoriasis:
- Managing inflammation: Follow the treatment prescribed by the dermatologist to reduce inflammation and alleviate psoriasis symptoms. Proper treatment can prevent scalp damage and hair loss.
- Avoid scratching: Try to avoid scratching the scalp, even if the itching is intense. Use soothing and moisturizing products to reduce itching and discomfort.
- Use gentle products: Use gentle shampoos and treatments, free of harsh chemicals, to maintain the health of the scalp and hair. Medicated shampoos specially formulated for scalp psoriasis can help reduce scaling and inflammation.
- Take care of your scalp: Keep the scalp hydrated using emollients and natural oils, such as coconut oil or jojoba oil. This can help prevent dryness and irritation.
- Consult a dermatologist: If you notice excessive hair loss or if scalp psoriasis symptoms do not improve, consult a dermatologist to adjust the treatment plan and receive additional advice.
The frequency of hair washing for people with scalp psoriasis can vary depending on the severity of symptoms and the recommendations of the dermatologist. However, there are some general guidelines that can help manage symptoms and maintain scalp health:
1. Wash your hair regularly, but not excessively
In general, it is recommended to wash your hair 2-3 times a week. Regular washing helps remove flakes and keep the scalp clean, which can reduce itching and inflammation. However, excessive washing can dry out the scalp and worsen psoriasis symptoms.
2. Use medicinal shampoos
For managing scalp psoriasis, use specially formulated shampoos that contain active ingredients such as salicylic acid, coal tar, ketoconazole, or corticosteroids. These shampoos can help reduce scaling, inflammation, and itching. Follow the instructions on the label and your doctor's recommendations regarding the frequency of use of these products.
3. Hydrate the scalp
After washing, apply a moisturizing conditioner or a scalp care treatment to prevent dryness and irritation. You can use products that contain soothing ingredients, such as aloe vera, coconut oil, or jojoba oil.
4. Avoid harsh and irritating products
Choose gentle hair care products without fragrances, dyes, or harsh chemicals. These can reduce the risk of irritation and worsening of psoriasis symptoms.
5. Gentle scalp massage
When washing your hair, gently massage the scalp to remove flakes without causing injury. Avoid scratching or aggressively rubbing the scalp, as this can worsen inflammation and itching.
6. Consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations
Each person with scalp psoriasis has different needs, so it is important to discuss with your dermatologist for personalized recommendations. The doctor can adjust the frequency of hair washing and recommend specific products depending on the severity of symptoms and the individual response to treatment.
Well, it is not mandatory to have psoriasis on the scalp if you have psoriasis on the body and vice versa. Psoriasis can appear isolated on certain areas of the body or can affect multiple regions simultaneously. Each person with psoriasis may have a different pattern of disease manifestation.
Individual manifestations of psoriasis:
1. Psoriasis on the scalp:
Scalp psoriasis is characterized by thick, red plaques covered with silvery scales that appear on the scalp. It can occur independently or together with psoriasis in other parts of the body.
2. Psoriasis on the body:
Psoriasis on the body can appear in different forms, including plaque psoriasis (the most common type), guttate psoriasis (characterized by small, drop-like spots), inverse psoriasis (which affects skin folds), and pustular psoriasis (characterized by white pustules).
Factors influencing the localization of psoriasis:
- Genetics: Family history can play a role in the predisposition to certain types of psoriasis and affected areas.
- Triggers: Trigger factors, such as stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications, can influence where and how psoriasis appears.
- Severity of the disease: People with severe psoriasis may have lesions on multiple areas of the body, including the scalp, while those with milder forms may have lesions limited to a single region.
1. Scalp psoriasis:
- Thick, red plates covered with silvery scales.
- The edges of the plates are well defined.
- Intense itching and possible pain.
It often affects other areas of the body as well (elbows, knees, lower back).
2. Seborrheic dermatitis:
- Greasy, yellowish or white flakes.
- Thinner and less defined plates.
- Moderate itching.
Appears in areas rich in sebaceous glands (scalp, face, chest).
3. Dandruff:
- White, dry flakes that easily fall off the scalp.
- No significant inflammation or redness.
- Mild to moderate itching.
It does not affect other areas of the body.
In case of uncertainty, consulting a dermatologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Yes, you can go to the pool if you have psoriasis, but it is important to take some precautions to protect your skin and to ensure that the experience is as comfortable as possible. Here are some tips:
1. Hydrate your skin before swimming
Apply a moisturizing cream or an emollient ointment before entering the water to create a protective barrier on the skin.
2. Avoid pools with excessive chlorine
Chlorine can irritate the skin and may worsen psoriasis symptoms. If the pool has a strong chlorine smell, it might be helpful to look for another option.
3. Rinse off after swimming
After you get out of the pool, rinse your skin with clean water to remove chlorine or other chemicals. Apply a moisturizing cream again after rinsing and drying.
4. Avoid scratches and excessive rubbing
Be careful not to scratch or rub your skin excessively, especially if your symptoms are active. Use a soft towel to dry yourself.
5. Monitor your skin
Pay attention to how your skin reacts to swimming and adjust your skincare routine accordingly. If you notice that the symptoms worsen, consult your dermatologist.
6. Choose a saltwater pool
Saltwater pools can be gentler on the skin than those with chlorine. Saltwater can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
Learn more about swimming in the pool if you suffer from psoriasis by accessing the link.
Yes, in general, it is safe to swim in the sea if you have psoriasis, and in fact, many people with this condition find that seawater can bring them benefits. However, it is important to take some precautions to ensure that your experience is as pleasant and beneficial as possible.
Benefits of seawater for psoriasis:
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties:
Salts and minerals in seawater, such as magnesium, can help reduce inflammation and prevent skin infections.
- Natural hydration and exfoliation:
Sea water can help remove scales and hydrate the skin, which can alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis.
- Exposure to the sun:
Swimming in the sea is often accompanied by moderate sun exposure, which can help alleviate psoriasis due to the beneficial effects of ultraviolet rays on the skin. It is important to use appropriate sunscreen to avoid sunburn.
Learn more about the benefits of saltwater for psoriasis by clicking the link.
To see benefits in alleviating psoriasis, exposure to seawater 2-3 times a week is generally recommended. This frequency can help reduce inflammation, hydrate the skin, and remove scales. However, each person is different, so it is important to monitor how your skin reacts and adjust the frequency as needed. If you have specific questions, consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
- Rinse with clean water: Removes salts and other substances from seawater.
- Apply a moisturizing cream: Use a moisturizer to keep the skin soft and hydrated.
- Avoid rubbing: Dry yourself with a soft towel, without rubbing the skin aggressively.
- Hydrate yourself: Drink water to rehydrate from the inside.
Use soothing products: If you feel irritation, apply soothing products such as aloe vera gel.
These measures will help you maintain healthy skin and prevent dryness or irritation after swimming in the sea.
Prolonged exposure to seawater can lead to excessive drying of the skin, irritation, and itching. Additionally, the salts and minerals in the water can worsen psoriasis symptoms if the skin is not properly moisturized after swimming. In some cases, prolonged sun exposure associated with swimming in the sea can cause sunburns, which can aggravate inflammation and discomfort of the skin affected by psoriasis. To minimize these side effects, it is important to rinse with clean water after swimming, apply a moisturizing cream, and use appropriate sun protection.
If you have psoriasis, it is important to pay attention to your diet, as certain foods can worsen inflammation and the symptoms of this condition.
In general, you should avoid processed and sugar-rich foods, such as sweets, soft drinks, and pastries, as they can increase inflammation in the body.
It is also recommended to reduce the consumption of red meat and foods high in saturated fats, such as fatty meat, full-fat dairy products, and fried foods, which can worsen inflammation.
Alcohol is another factor that can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, so limiting alcohol consumption may be beneficial.
Gluten, found in wheat, barley, and rye, can be a trigger for some people with psoriasis, although the link is not clear for all patients. Also, some people may have sensitivities to nightshades, such as tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, and eggplants, so monitoring reactions to these foods may help manage symptoms.
Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and consult a specialist for personalized advice related to your diet.
Psoriasis and eczema are both inflammatory skin conditions, but they differ in causes, symptoms, and location. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that accelerates the growth of skin cells, resulting in thick, red plaques covered with silvery scales, and commonly appears on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is related to a defective skin barrier and a hyperactive immune response to allergens and irritants, manifesting as red patches, intense itching, which can be wet or dry and scaly, often affecting skin folds such as the elbows, knees, and neck. While psoriasis tends to be a chronic condition with episodes of remission and flare-ups, eczema can vary in severity and may be triggered by allergic factors and environmental irritants.
Psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, as it is an autoimmune condition with a strong genetic component. However, certain measures can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Managing stress, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding known triggers (such as certain medications, infections, and skin injuries), and proper skin care can contribute to controlling symptoms and preventing relapses. Regular consultation with a dermatologist for monitoring and adjusting treatment is also essential.
Yes, warm and sunny climates can help alleviate psoriasis. Moderate sun exposure can reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells due to the beneficial effects of ultraviolet (UV) rays. Additionally, moderate humidity can prevent excessive skin dryness, which can reduce irritation. However, it is important to avoid excessive sun exposure and to use appropriate sunscreen to prevent sunburns, which can worsen the symptoms.
Managing psoriasis during pregnancy requires a careful and tailored approach to protect both the mother's and the baby's health. It is essential to work closely with the dermatologist and obstetrician to adjust treatments based on their safety during pregnancy. Many topical treatments, such as moisturizing creams and emollients, are safe and can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce itching. Topical corticosteroids can be used cautiously, in small doses and for short periods. Systemic and biological treatments must be evaluated individually, as some may be contraindicated during pregnancy. Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and light exercise, can help alleviate symptoms, as stress is a common trigger for psoriasis. It is important to avoid exposure to irritants and maintain a balanced diet to support overall health. Regular consultations with doctors and careful monitoring of health status are crucial to effectively manage psoriasis during pregnancy.
To learn more, read the article about managing psoriasis during pregnancy.
Alcohol can worsen psoriasis by increasing inflammation and impairing the immune system. Alcohol consumption can reduce the effectiveness of treatments and can trigger relapses or worsen symptoms. Additionally, alcohol can negatively interact with medications used to treat psoriasis, increasing the risk of side effects. Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption can help manage psoriasis symptoms more effectively.
To learn more, read the article about the impact of alcohol on psoriasis.
Psoriasis does not necessarily worsen with age, but the progression of the disease can vary considerably from one person to another. In some individuals, symptoms may remain stable or even improve over time, while in others, the disease may have episodes of worsening and remission. Factors such as stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications can influence the severity of psoriasis. Additionally, comorbidities associated with aging, such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes, can complicate the management of psoriasis. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, following prescribed treatments, and regular consultations with a dermatologist can help control symptoms in the long term.
Yes, you can exercise if you have psoriasis, and in fact, exercise can bring numerous benefits for managing this condition. Regular physical activity helps reduce inflammation, improve mood, and manage stress, which is a common trigger for psoriasis. It is important to choose exercises that do not irritate the skin and to wear comfortable clothing that allows the skin to breathe. Avoid activities that may cause friction or trauma to the skin. After exercising, it is essential to take a shower and apply a moisturizing cream to keep the skin healthy and hydrated.
The decision to inform your employer and colleagues about your psoriasis is a personal one and depends on several factors. Informing the employer can be beneficial because they can provide additional support and make adjustments at the workplace to improve comfort and productivity. For example, the employer may allow extra breaks for applying topical treatments or adapt the work environment to reduce irritant factors.
Disclosing information to colleagues can help reduce stigma and create a more understanding and supportive work environment. However, it is important to feel comfortable with this decision and to assess the culture and dynamics of your workplace.
On the other hand, if you feel that disclosure could lead to discrimination or unfair treatment, you have the right to keep your medical confidentiality. Before making a decision, it may be helpful to discuss with a human resources specialist or a counselor to evaluate the best options for your specific situation.
Well, you shouldn't be fired just because you have psoriasis. Workplace discrimination laws protect people with medical conditions, including psoriasis.
Article 16 of the Romanian Constitution - Equality in Rights
Article 16 of the Romanian Constitution prohibits any form of discrimination, including on the grounds of illness. Here is the full text of this article:
Article 16: Equality in rights
(1) Citizens are equal before the law and public authorities, without privileges and without discrimination.
(2) No one is above the law.
(3) Public, civil, or military functions and dignities may be held, under the conditions of the law, by persons who have Romanian citizenship and domicile in the country.
(4) Under the conditions of Romania's accession to the European Union, Union citizens who meet the requirements of the organic law have the right to vote and to be elected in local public administration authorities.
This article ensures equality of rights for all Romanian citizens, prohibiting discrimination of any kind, including on the basis of illness, and guarantees that all citizens are treated equally before the law and public authorities.
Article 5 of the Labor Code - Equality of treatment
In Romania, the Labor Code (Law no. 53/2003) also provides for the prohibition of discrimination on various grounds, including on the basis of illness. Here is the relevant text:
Article 5: Equality of treatment
(1) Within labor relations, the principle of equal treatment applies to all employees and employers.
(2) Any direct or indirect discrimination against an employee based on sex, sexual orientation, genetic characteristics, age, national origin, race, color, ethnicity, religion, political opinion, social origin, disability, family situation or responsibility, trade union membership or activity, is prohibited.
(3) Direct discrimination occurs when a person is treated less favorably on the grounds of race, nationality, ethnicity, sex, sexual orientation, genetic characteristics, age, national origin, race, color, ethnicity, religion, political opinion, social origin, disability, family situation or responsibility, trade union membership or activity than another person in a comparable situation.
(4) Indirect discrimination occurs when a provision, criterion, or practice, apparently neutral, would particularly disadvantage a person compared to others, based on race, nationality, ethnicity, sex, sexual orientation, genetic characteristics, age, national origin, race, color, ethnicity, religion, political opinion, social origin, disability, family situation or responsibility, trade union membership or activity, except where this provision, criterion, or practice is objectively justified by a legitimate aim, and the means of achieving that aim are appropriate and necessary.
This article emphasizes the prohibition of any form of discrimination in employment relationships, ensuring equal treatment for all employees, including on grounds of illness.
Learn more about how to avoid discrimination at the workplace for psoriasis by accessing the link.
Your emotional and practical support can make a significant difference in the life of a person suffering from psoriasis. Here are some tips on how to provide the necessary help:
1. Educate yourself about psoriasis
Start by learning about psoriasis. Understanding the disease, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments will help you be more empathetic and effective in providing support. Inform yourself about the triggers, such as stress, certain foods, or medications, so you can help avoid them.
2. Provide emotional support
Psoriasis can have a profound emotional impact. Listen and offer a shoulder to lean on. Be patient and understanding when your loved one goes through difficult times. Validate their feelings and encourage them to talk about their experiences.
3. Avoid stigmatization and myths
Avoid making negative comments or perpetuating myths about psoriasis. Make sure your loved one knows that the disease is not contagious and that they should not feel embarrassed or ashamed of their condition.
4. Support them in managing the treatment
Help your loved one follow the treatment plan recommended by the doctor. This may include reminding them to apply topical creams, accompanying them to medical appointments, or supporting them in taking oral or injectable medication.
5. Improve lifestyle
Encourage adopting a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet, regular physical exercise, and stress reduction techniques can help alleviate symptoms. Participate in activities that promote health and overall well-being, such as outdoor walks, yoga, or cooking healthy meals together.
6. Adapt the environment for comfort
Make sure the home environment is comfortable for someone with psoriasis. Keep a humidifier to prevent skin dryness, provide appropriate skincare products, and avoid harsh cleaning products that could irritate the skin.
7. Encourage participation in support groups
Support groups can be very helpful for people suffering from psoriasis. Encourage them to participate in such groups, either in person or online, where they can share experiences and find support from others who understand what they are going through.
8. Respect privacy and autonomy
Respect the wishes and boundaries of your loved one. If they do not want to talk about their illness or receive help at certain times, respect their privacy and autonomy.
9. Pay attention to signs of depression or anxiety
Psoriasis can contribute to mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety. Be attentive to the signs of these conditions and encourage the person to seek professional help if necessary.
10. Be a constant ally
Providing constant support is essential. It shows that you are there for them in the long term, regardless of fluctuations in the severity of symptoms.
Blog articles
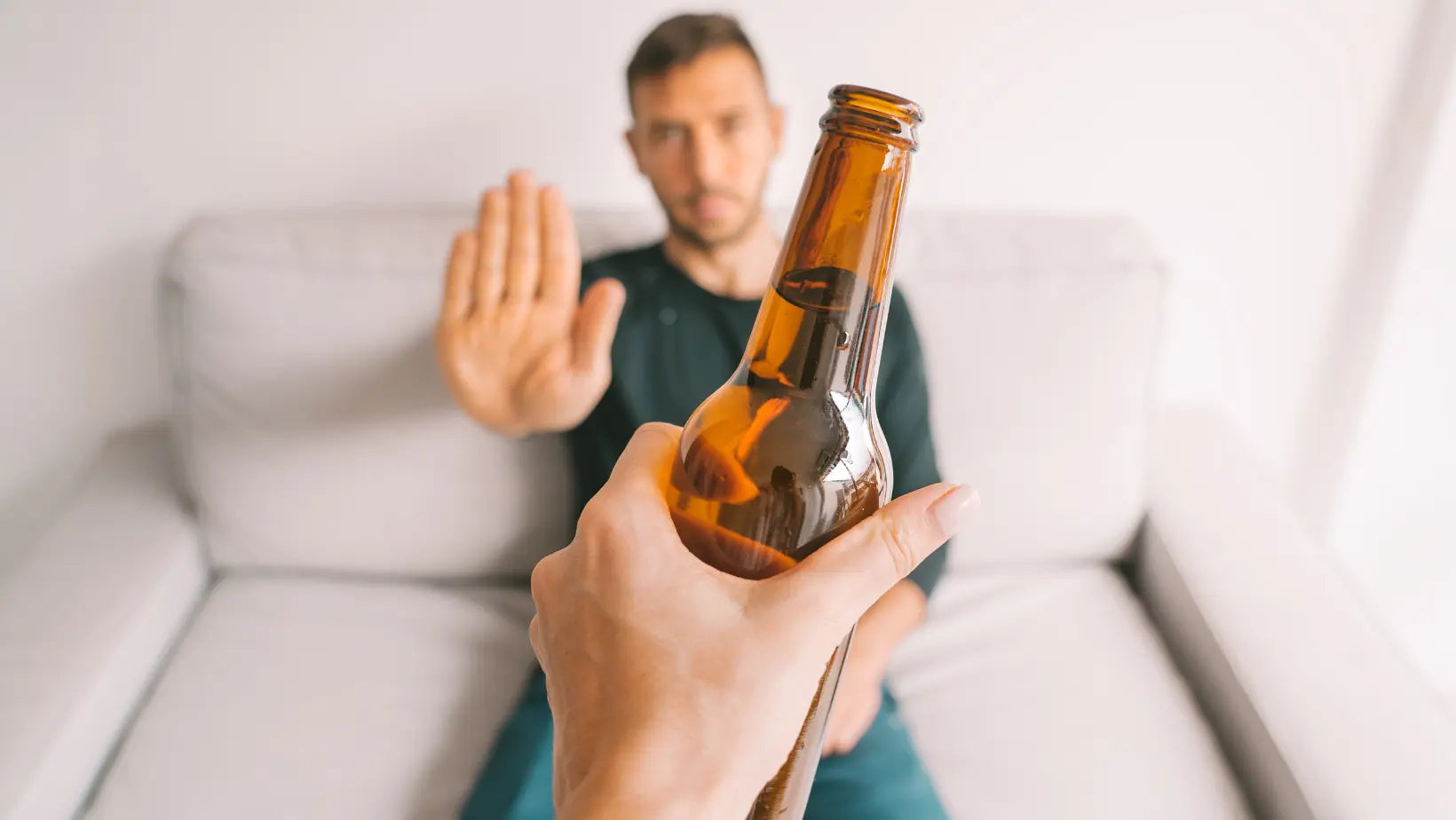

The impact of alcohol on psoriasis: What you need to know
Understanding how alcohol affects psoriasis is essential for anyone dealing with this condition. Alcohol consumption can worsen psoriasis symptoms and complicate treatment. Often, patients do not r...
Read more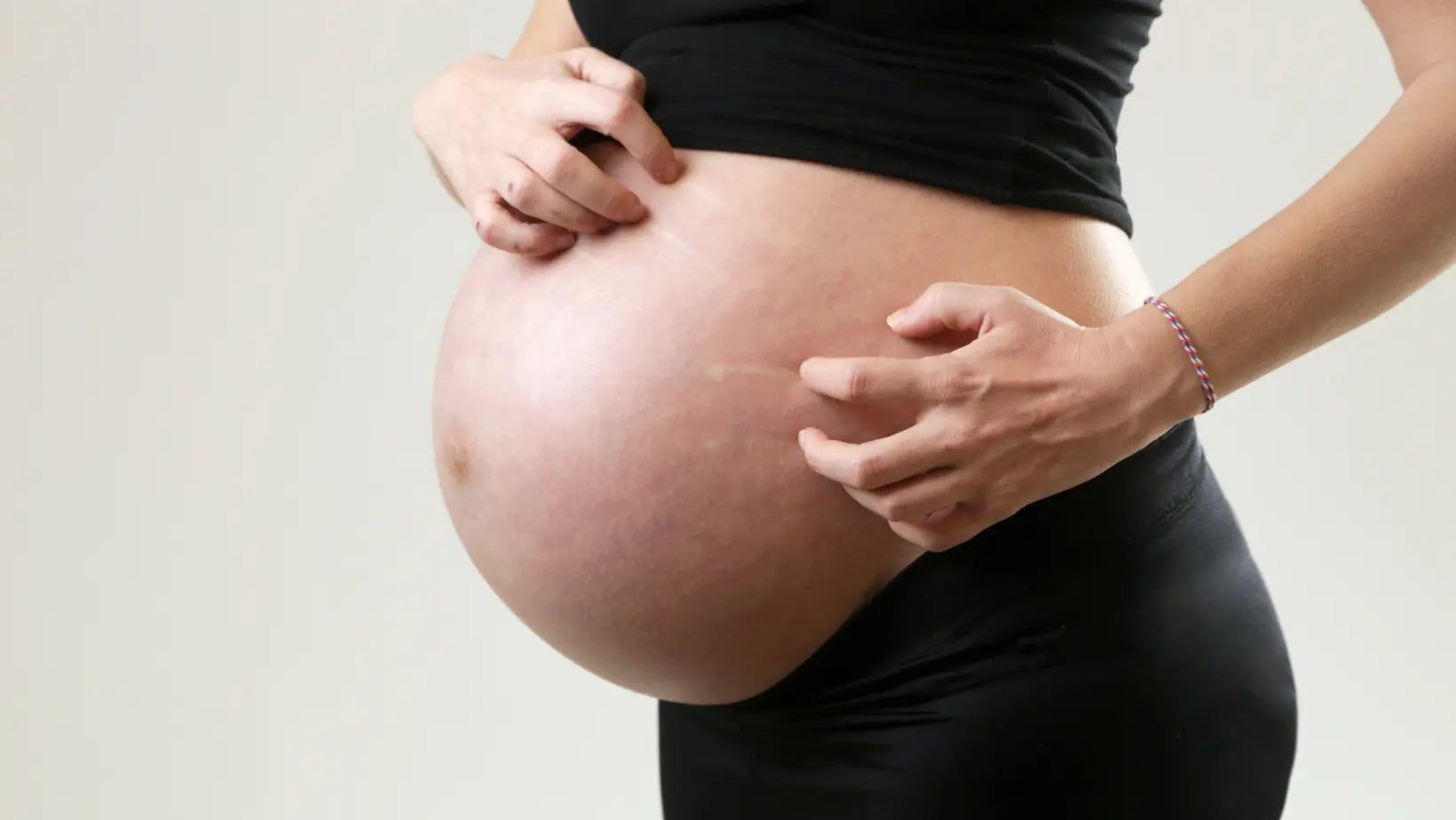
How to manage psoriasis during pregnancy
Pregnancy is one of the most beautiful and special periods in your life, but it can also bring challenges, especially if you are dealing with psoriasis. It is essential to discuss managing psoriasi...
Read more
Psoriasis: A dermatological condition with possible complications for the entire body
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by the appearance of red plaques covered with silvery scales, which can cause itching or pain. This autoimmune disease accelerates the life cycle...
Read more





